Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
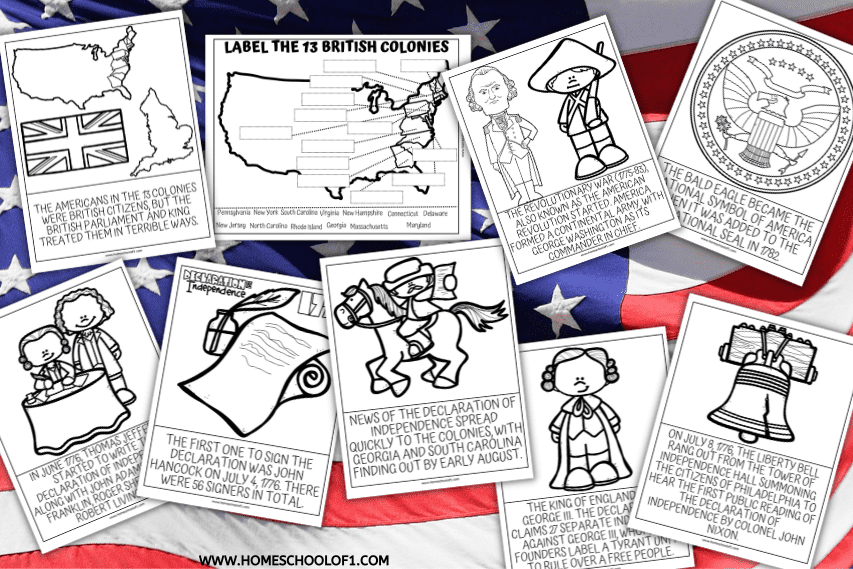
The Declaration of Independence, adopted on July 4, 1776, is one of the most significant documents in world history, marking the birth of the United States as a sovereign nation and laying the foundation for modern democratic principles. After two days of editing and debate, the Congress adopted the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776, even as a large British fleet and more than 34,000 troops prepared to invade New The definition of the Declaration of Independence for APUSH is a foundational document adopted by the Second Continental Congress on July 4, 1776. Drafted primarily by Thomas Jefferson, it announced the independence of the 13 Original Colonies from British rule. The Declaration of Independence is the foundational document of the United States of America. Written primarily by Thomas Jefferson, it explains why the Thirteen Colonies decided to separate from Great Britain during the American Revolution (1765-1789). Declaration of Independence - Founding Document, US History, Revolutionary War: The Declaration of Independence was written largely by Jefferson, who had displayed talent as a political philosopher and polemicist in his A Summary View of the Rights of British America, published in 1774. At the request of his fellow committee members he wrote the first draft. The members of the committee made a On the one hand, the Declaration was a formal legal document that announced to the world the reasons that led the thirteen colonies to separate from the British Empire. Much of the Declaration sets forth a list of abuses that were blamed on King George III. In this week's Libertarian Angle, Jacob and Richard discuss the real significance of the Declaration of Independence.Go to the podcast.Please subscribe to ou Declaration of Independence, in U.S. history, document that was approved by the Continental Congress on July 4, 1776, and that announced the separation of 13 North American British colonies from Great Britain. The introductory sentence states the Declaration’s main purpose, to explain the colonists’ right to revolution. In other words, “to declare the causes which impel them to the separation.” Congress had to prove the legitimacy of its cause. It had just defied the most powerful nation on Earth. The Declaration of Independence and the Constitution are cornerstones of American democracy, embodying fundamental ideals that continue to shape the nation. The Declaration emphasizes natural rights, equality, and the right to revolt, establishing a framework for a government accountable to its people. The Constitution builds on these principles with mechanisms like separation of powers The Declaration was a formal explanation of why the Continental Congress voted to declare American independence from the Kingdom of Great Britain. It was adopted by the Congress during the American Revolutionary War, which commenced in April 1775 with the Battles of Lexington and Concord. The Declaration of Independence, 1776 By issuing the Declaration of Independence, adopted by the Continental Congress on July 4, 1776, the 13 American colonies severed their political connections to Great Britain. The Declaration summarized the colonists’ motivations for seeking independence. Of course the British were unwilling to walk away without a fight, so the Declaration of Independence eventually led to the American Revolutionary War. Signed on July 4, 1776, the Declaration of Independence is considered the birthday of our nation. Declaring Independence On July 2, 1776, Congress voted to declare independence. Two days later, it ratified the text of the Declaration. John Dunlap, official printer to Congress, worked through the night to set the Declaration in type and print approximately 200 copies. Within the U.S., the women’s suffrage movement adapted the Declaration of Independence for their cause, asserting in the 1848 Declaration of Sentiments that “all men and women are created equal.” On July 4, 1776, the United States officially declared its independence from the British Empire when the Second Continental Congress adopted the Declaration of Independence. The Declaration was authored by a “Committee of Five”—John Adams, Benjamin Franklin, Thomas Jefferson, Robert Livingston, and Roger Sherman—with Jefferson as the main drafter. But Jefferson himself later admitted These three documents, known collectively as the Charters of Freedom, have secured the rights of the American people for more than two and a quarter centuries and are considered instrumental to the founding and philosophy of the United States. Declaration of Independence Learn More The Declaration of Independence expresses the ideals on which the United States was founded and the reasons for Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which of the following writers did not directly influence Jefferson's writing of the Declaration of Independence?, Which is not a characteristic of Thomas Jefferson according to Historian Joseph Ellis?, Thomas Jefferson was born in and more. The rhetorical question posed by Frederick Douglass in the excerpt, "Are the great principles of political freedom and of natural justice, embodied in that Declaration of Independence, extended to us?", plays a crucial role in emphasizing the exclusion of African Americans from the rights outlined in the Declaration of Independence. Discuss the significance of the Preamble in the Declaration of Independence and how it sets the tone for the rest of the document.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |