Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
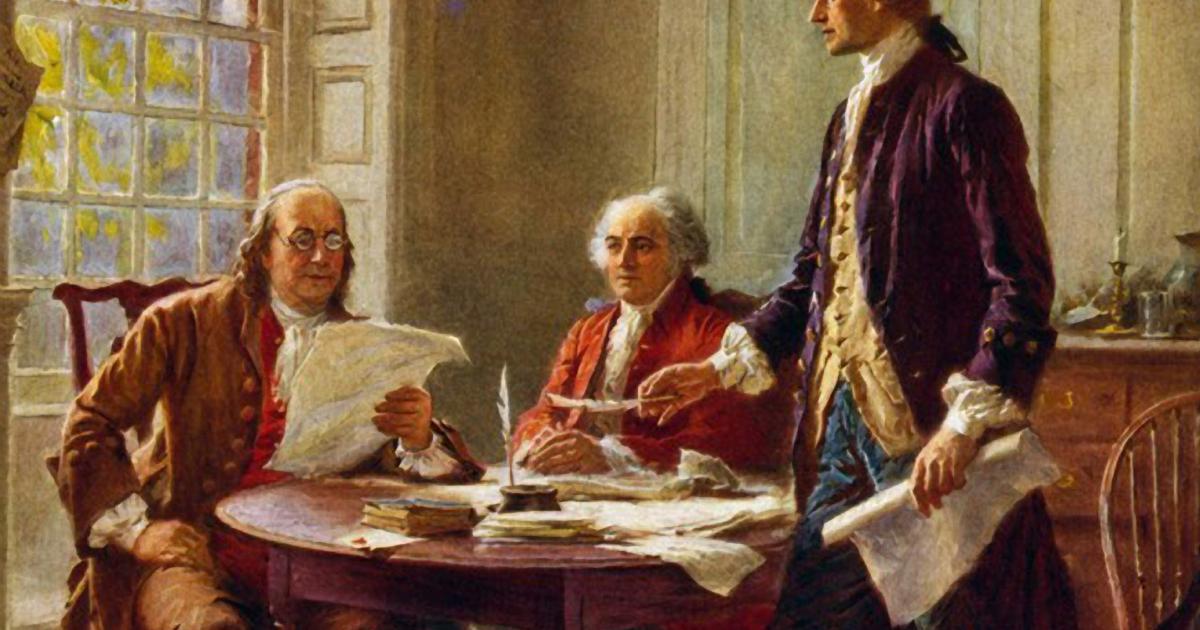
The Declaration of Independence states three basic ideas: (1) God made all men equal and gave them the rights of life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness; (2) the main business of government is to protect these rights; (3) if a government tries to withhold these rights, the people are free to revolt and to set up a new government. 13a. The Declaration of Independence and Its Legacy "When in the Course of human events, it becomes necessary for one people to dissolve the political bands which have connected them with another, and to assume among the powers of the earth, the separate and equal station to which the Laws of Nature and of Nature's God entitle them, a decent respect to the opinions of mankind requires that We will discuss two principles of paramount significance: 1) The truth that our rights come from God; and 2) the reality that political power springs from the People and exists for the purpose of securing their God-given rights. The document is divided into three main parts: the Preamble, the Declaration of Natural Rights, and the List of Grievances. The Preamble outlines the philosophical foundation of the document, emphasizing the principles of equality and the rights to life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. The Declaration of Independence states the principles on which our government, and our identity as Americans, are based. Unlike the other founding documents, the Declaration of Independence is not legally binding, but it is powerful. Note: The following text is a transcription of the Stone Engraving of the parchment Declaration of Independence (the document on display in the Rotunda at the National Archives Museum.) The spelling and punctuation reflects the original. Principle 3: The government gets it power to make decisions and protect rights from the people The Declaration of Independence states that "governments are instituted among men, driving their just power from the consent of the governed." On July 4, 1776, after two days of debate and editing, the Continental Congress adopted the Declaration of Independence submitted by the Committee of Five. The Declaration of Independence is made up of three major parts: the preamble; the body, and the conclusion. These three documents, known collectively as the Charters of Freedom, have secured the rights of the American people for more than two and a quarter centuries and are considered instrumental to the founding and philosophy of the United States. Declaration of Independence Learn More The Declaration of Independence expresses the ideals on which the United States was founded and the reasons for The Continental Congress adopted the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776. It was engrossed on parchment and on August 2, 1776, delegates began signing it. Below one can read the original text, as well as consult three annotated versions explaining the Declaration's basic principles, its historical context, and a glossary of terms. The Declaration of Independence included these three major ideas: People have certain Inalienable Rights including Life, Liberty and Pursuit of Happiness. All Men are created equal. On July 4, 1776, the United States officially declared its independence from the British Empire when the Second Continental Congress adopted the Declaration of Independence. The Declaration was authored by a “Committee of Five”—John Adams, Benjamin Franklin, Thomas Jefferson, Robert Livingston, and Roger Sherman—with Jefferson as the main drafter. But Jefferson himself later admitted In 1987 the National Archives and Records Administration installed a $3 million camera and computerized system to monitor the condition of the three documents. The Charters Monitoring System was designed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory to assess the state of preservation of the Constitution, the Declaration of Independence, and the Bill of Rights. On July 4, 1776, the United States officially declared its independence from the British Empire when the Second Continental Congress adopted the Declaration of Independence. The Declaration was authored by a “Committee of Five”—John Adams, Benjamin Franklin, Thomas Jefferson, Robert Livingston, and Roger Sherman—with Jefferson as the main drafter. But writing to Henry Lee in 1825 Declaration of Independence, 17761 IN CONGRESS, July 4, 1776 The unanimous Declaration of the thirteen united States of America, Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like The authors of the Declaration of Independence, Which Congress adopted the Declaration of Independence?, The Declaration of Independence and more. The Declaration of Independence and the Constitution are cornerstones of American democracy, embodying fundamental ideals that continue to shape the nation. The Declaration emphasizes natural rights, equality, and the right to revolt, establishing a framework for a government accountable to its people. The Constitution builds on these principles with mechanisms like separation of powers The Declaration of Independence included these three major ideas: People have certain Inalienable Rights including Life, Liberty and Pursuit of Happiness. All Men are created equal. The Declaration of IndependenceOne of twenty-four surviving copies of the first printing of the Declaration of Independence done by Philadelphia printer John Dunlap in the evening of July 4, 1776.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |