Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
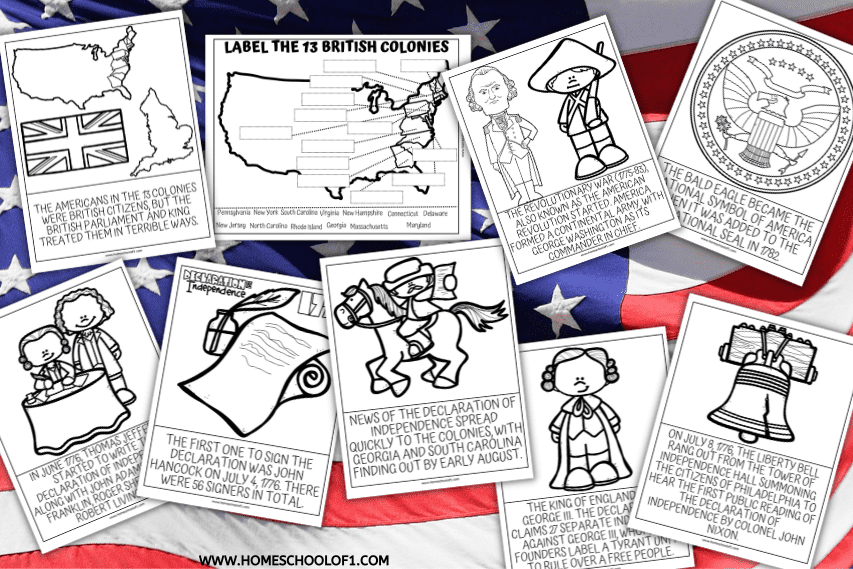
The Declaration made the case that the British Monarchy had given up its right to rule the American colonies based on King George III’s failures. Congress hoped this would convince other monarchies to assist the newly independent states without encouraging similar rebellions in their own countries. Why did colonists feel the Articles of Confederation were necessary even though the Declaration of Independence was already written? A) The Declaration of Independence outlined a system of government but did not specify how much power that government could have. B) The Declaration of Independence determined individual rights but did not discuss how those rights influenced others. C) The Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like In the Declaration of Independence, Thomas Jefferson listed a series of grievances that colonists had against British rule. What purpose did this serve? -The list identified changes that would be made under the new government. -The list explained the reasons for declaring This page shows the changes made over the course of the Declaration’s drafting and revisions. Specifically, it details the changes that occured between when Jefferson wrote his rough draft and the revision that was ultimately approved by Congress on 4 July 1776. Timeline of significant events related to the Declaration of Independence. The document proclaimed that the 13 original colonies of America were “free and independent states.” It was the last of a series of steps that led the colonies to final separation from Great Britain. After the United States declared its independence from the British in 1776, the country embarked on a journey to create its own laws and institutions. At first, Americans were ruled by multiple state constitutions, but soon became evident the need for a strong central government with a single constitution for the whole nation, drafted in 1787. The Declaration of Independence is the foundational document of the United States of America. Written primarily by Thomas Jefferson, it explains why the Thirteen Colonies decided to separate from Great The Declaration of Independence, formally The unanimous Declaration of the thirteen united States of America in the original printing, is the founding document of the United States. On July 4, 1776, it was adopted unanimously by the Second Continental Congress, who convened at Pennsylvania State House, later renamed Independence Hall, in the colonial capital of Philadelphia. These delegates The story behind the Great Compromise—the 1787 deal that made the U.S. possible A deadlock over the distribution of power threatened to derail the creation of a constitution for the newly formed After the war, the Declaration’s vision was embodied in the 13th, 14th, and 15th Amendments to the Constitution, which formally ended slavery, guaranteed all persons the “equal protection of the laws,” and gave African-American men the right to vote. SUMMARY On July 4, 1776, the United States officially declared its independence from the British Empire when the Second Continental Congress adopted the Declaration of Independence. The Declaration was authored by a “Committee of Five”—John Adams, Benjamin Franklin, Thomas Jefferson, Robert Livingston, and Roger Sherman—with Jefferson as the main drafter. But Jefferson himself later The Continental Congress adopted the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776. It was engrossed on parchment and on August 2, 1776, delegates began signing it. These three documents, known collectively as the Charters of Freedom, have secured the rights of the American people for more than two and a quarter centuries and are considered instrumental to the founding and philosophy of the United States. The Reconstruction Amendments, encompassing the 13th, 14th, and 15th amendments, are monumental additions to the United States Constitution. These amendments were ratified in the turbulent post-Civil War era, a period marked by profound societal transformation and the urgent need for legal structures that would redefine freedom and equality in America. They were designed to address the Who refused to write the Declaration of Independence because he feared that his reputation for humor would distract from the document's purpose? Benjamin Franklin Why did Congress want a written Declaration of Independence? The colonies wanted help from other nations in Europe. The soldiers needed a good reason for fighting and dying. However, the road to independence was long and difficult, and the aftermath of the revolution was filled with its own unique set of challenges. In this article, we will examine the difficulties faced by the new United States in the aftermath of the American Revolution. The Declaration of Independence is made up of three major parts: the preamble; the body, and the conclusion. The preamble of the Declaration of Independence establishes a philosophical justification for a split with Britain — all men have rights, the government is established to secure those rights, if and when such government becomes a The Declaration of Independence, which oficially broke all political ties between the American colonies and Great Britain, set forth the ideas and principles behind a just and fair government, and the Constitution outlined how this government would function. He has obstructed the Administration of Justice by refusing his Assent to Laws for establishing Judiciary Powers. He has made Judges dependent on his Will alone for the tenure of their offices, and the amount and payment of their salaries. Almost forgotten today, the Declaration and Resolves were a precursor to both the Declaration of Independence and the Bill of Rights. It reaffirmed that acts beyond the Constitution are void and must be resisted and nullified.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |